Domain-Based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance (DMARC): Your Ultimate Email Security Shield
In the current digital era, email is still the mainstay of corporate communications. However, this all-important channel has been a prime target for cyber attackers. Moreover, email spoofing and phishing attacks are still posing threats to businesses worldwide.
Enter Domain-Based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance (DMARC), a highly effective solution to fight these threats. Moreover, this thorough email authentication protocol gives businesses everything they require to ensure their domain reputation and defend their email communication effectively.
What is Domain-Based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance (DMARC)?
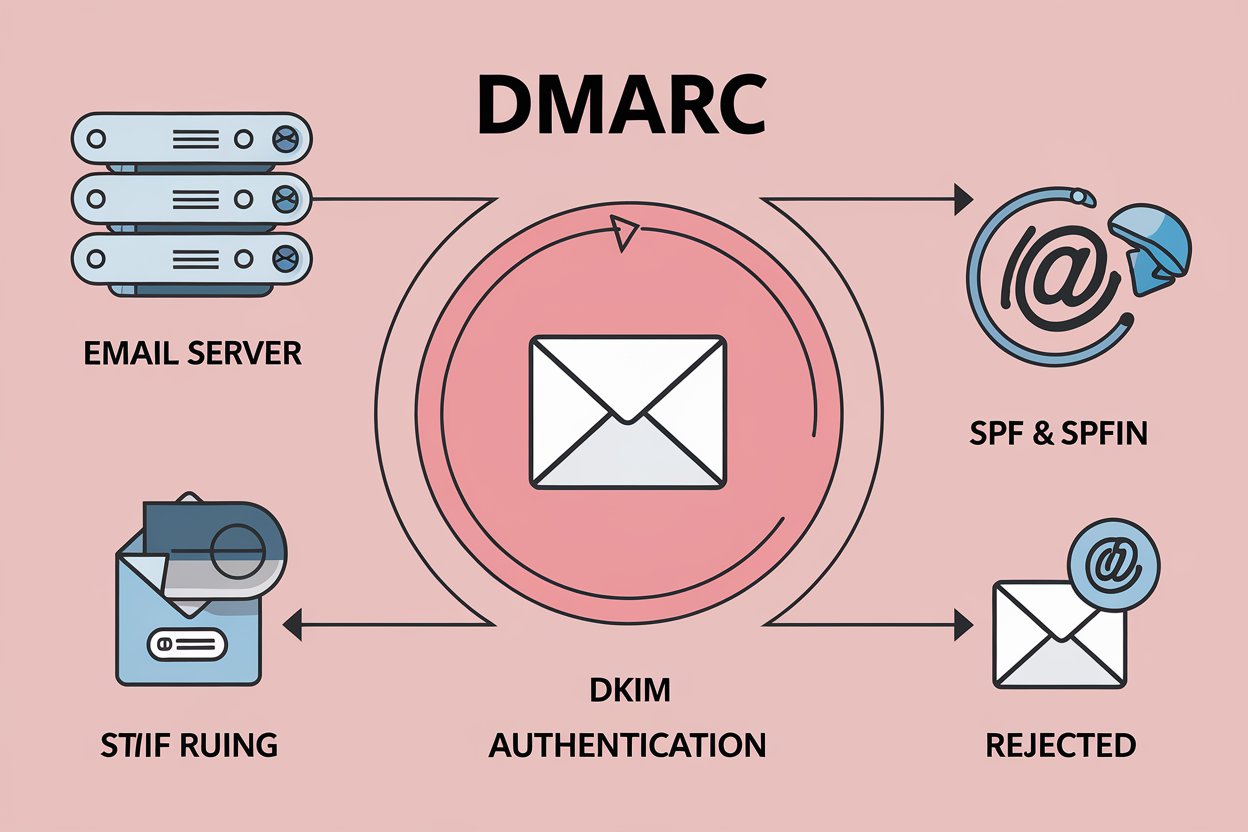
DMARC is an abbreviation for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, a technique of email authentication that aims to provide email domain owners with the capability to safeguard their domain against unauthorized usage. This security protocol leverages two established email authentication systems: SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail).
Key Components of DMARC
First, knowledge of the basic building blocks enables organizations to apply DMARC successfully. Furthermore, the protocol has three fundamental components:
- Authentication: Verifies email legitimacy through SPF and DKIM
- Policy: Defines actions for failed authentication
- Reporting: Provides detailed feedback on email authentication results
How DMARC Works: The Technical Foundation
DMARC authenticates the senders of emails based on the Domain Name System (DNS), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) protocols. In addition, the authentication process has a number of related steps.
The DMARC Authentication Process
First, upon the receipt of an email to the recipient server, the system checks DMARC policy. Second, it conducts SPF and DKIM authentication tests. Third, the system assesses alignment between the “From” domain and authenticated domains. Fourth, depending on the DMARC policy, the email is delivered, quarantined, or rejected.
Essential DMARC Policy Options
Three main DMARC policies can be implemented by organizations. Additionally, each policy provides varying degrees of protection and implementation options.
DMARC Policy Types
None (Monitor)
- Monitors email authentication without taking action
- Provides valuable reporting data
- Ideal for the initial implementation phase
Quarantine
- Places suspicious emails in the spam folder
- Balances security with email deliverability
- Recommended for organizations gaining confidence
Reject
- Blocks unauthenticated emails completely
- Provides maximum security protection
- Suitable for organizations with mature email authentication
Benefits of Implementing DMARC
DMARC safeguards against bad actors employing spoofed email addresses designed to appear as authentic messages from known sources. Moreover, organizations have many benefits to accrue from correct adoption of it.
Security Benefits
To start with, DMARC considerably lowers phishing attacks on your domain. Second, its stops email spoofing as well as brand impersonation. Third, the protocol enhances email security posture overall. In addition, organizations receive precise visibility into email authentication status.
Business Benefits
In addition, DMARC implementation enhances email deliverability rates. Further, it safeguards brand reputation and customer trust. In addition, organizations realize improved compliance with industry regulations.
DMARC Implementation Best Practices
Successful DMARC deployment requires careful planning and execution. Moreover, organizations should follow proven implementation strategies to maximize effectiveness.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Assessment
- Audit the current email infrastructure
- Identify all legitimate email sources
- Implement SPF and DKIM if not already configured
Phase 2: Monitoring
- Deploy DMARC policy with “none” setting
- Analyze reporting data for several weeks
- Identify and authenticate legitimate sources
Phase 3: Enforcement
- Gradually increase policy enforcement
- Move from “none” to “quarantine” to “reject.”
- Monitor impact on email deliverability
Common DMARC Implementation Challenges
Organizations often face certain challenges while deploying it. Moreover, knowing these impediments ensures a successful implementation.
Technical Challenges
First, sophisticated email infrastructure tends to make its implementation a hassle. Second, third-party email providers might need special configuration. Third, aged systems could need to be upgraded to accommodate current authentication. Finally, DNS config errors can affect operation.
Organizational Challenges
Additionally, a lack of technical knowledge may hinder implementation progress. Moreover, coordination between more than one department is a task of careful planning. Again, balancing security and business continuity needs careful consideration.
DMARC Tools and Services
Several tools and services can assist organizations with DMARC implementation and management. Moreover, these solutions simplify the deployment process significantly.
Popular DMARC Tools
DMARC Analyzers
- Provide a detailed report analysis
- Offer implementation guidance
- Monitor ongoing performance
DNS Management Tools
- Simplify DMARC record creation
- Validate configuration accuracy
- Support policy updates
Email Security Platforms
- Integrate DMARC with comprehensive security
- Provide centralized management
- Offer automated policy adjustments
How OraSec Enhances Your Email Security Strategy
OraSec offers end-to-end cybersecurity solutions that pair perfectly with DMARC implementation. In addition, their penetration testing capabilities ensure that organizations discover email security vulnerabilities before malicious attackers make the most of them.
OraSec’s Email Security Services
To begin, OraSec’s pentesting experts analyze email infrastructure in depth. Next, they detect configuration vulnerabilities that may bypass DMARC protection. Third, their extensive reports offer actionable advice on how to bolster email security. Lastly, OraSec’s customized solutions work well to focus on particular organizational vulnerabilities.
Additionally, OraSec’s track record of 400+ global companies speaks well of their cybersecurity skills. In addition to this, their holistic solution keeps organizations strong on email security and DMARC implementation.
DMARC Reporting and Analytics
DMARC provides reporting capabilities that help domain owners understand how their email authentication is performing. Additionally, these reports offer valuable insights for ongoing security improvement.
Types of DMARC Reports
Aggregate Reports (RUA)
- Provide statistical summaries
- Show authentication results trends
- Help identify legitimate sources
Forensic Reports (RUF)
- Contain detailed failure information
- Include email headers and content
- Support specific incident investigation
Conclusion
Domain-Based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) is an important part of contemporary email security strategy. Additionally, correct implementation safeguards organizations against phishing, email spoofing, and brand impersonation. In addition, the combination of authentication, policy enforcement, and granular reporting allows for end-to-end email security coverage.
Organizations need to give top priority to DMARC adoption to secure their digital communications. Moreover, collaboration with cybersecurity professionals such as OraSec guarantees end-to-end security coverage beyond email validation. Thus, adopt DMARC today to secure your organization’s email communications and uphold customer confidence. Want to fortify your email security? Reach out to OraSec for professional cybersecurity consulting services and extensive penetration testing solutions that complement your DMARC adoption strategy.