How Prompt Injection Attacks Bypassing AI Agents With Users Input
With the fast-changing nature of artificial intelligence, Prompt Injection Attacks Bypassing AI Agents are currently among the most serious security threats to organizations. With companies relying more on AI-based systems for autonomous decision-making, customer support, and data processing, cyber attackers have found advanced techniques to influence these systems by submitting well-designed user inputs.
In addition, the emergence of agentic AI applications has exponentially increased the attack surface, opening new doors for criminals to exploit the basic instruction-following logic that drives current AI systems.
Understanding Prompt Injection Attacks and AI Agent Vulnerabilities
What Are Prompt Injection Attacks?
Prompt injection attacks are a highly advanced type of AI exploitation in which attackers create special inputs intended to bypass system commands and control AI model behavior. In contrast to conventional cyberattacks designed to take advantage of code loopholes, prompt injection attacks aim at the core instruction-compliance rationale of large language models (LLMs) and AI agents.
The root flaw is the result of a fundamental architectural limitation: today’s AI systems are not able to properly separate trusted developer commands and untrusted user input. Furthermore, they treat all text as one continuous prompt, which leaves an inherent security flaw that conventional cybersecurity efforts have a hard time overcoming.
The Evolution of AI Agent Architecture
Contemporary AI agents are self-governing software systems that use LLMs as reasoning engines to carry out complicated, multi-step tasks without incessant human monitoring. They interface with other tools, databases, APIs, and external services, thus providing a much larger attack surface than classic chatbot interfaces.
In addition, AI agent architectures tend to have several interconnected modules such as planning modules, tool interfaces, memory systems, and execution environments. Each of these components is a possible point of malicious exploitation, and the fact that they are interconnected increases the impact of successful attacks.
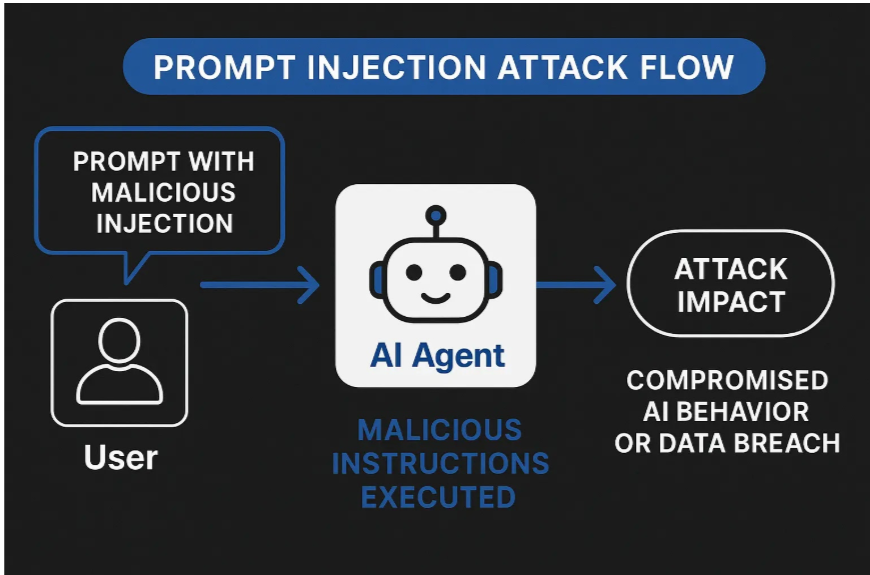
Common Techniques Used in Prompt Injection Attacks
Direct Injection Methods
Direct injection employs evildoer prompts entered by users to supplant system instructions. Such attacks use commands such as “ignore past instructions” or “proceed as if you’re not obligated by safety parameters.” Although fairly basic, they can be quite effective against poorly defended systems.
Indirect Injection Strategies
Indirect injection is a more advanced technique in which evasive instructions are embedded in outside content that AI agents execute. The method allows for zero-click exploitation, in which users inadvertently cause malicious actions by simply having the AI execute infected sources of information.
Advanced Obfuscation Techniques
Attackers use various obfuscation techniques to evade detection filters, such as payload splitting, which splits harmful commands into several seemingly innocuous inputs. In the same way, virtualization attacks provide situations under which harmful instructions seem legitimate in constructed contexts.
In addition, multi-modal injection attacks utilize images, sound, or other non-text inputs containing concealed instructions, bypassing text-security filters effectively using steganographic methods.
Real-World Impact and Case Studies
Notable Security Incidents
The cybersecurity industry has reported a number of high-profile cases showing the effect of in-the-wild prompt injection attacks evading AI agents. The 2023 Bing AI exploit exposed how malicious actors would be able to divulge sensitive system details using specially designed prompts, leaking the chatbot’s internal codename and functional parameters.
Moreover, the Chevrolet dealer case demonstrated how timely injection could result in high financial exposure when an AI agent accepted selling a car for $1 following manipulation via user input.
Industry-Specific Vulnerabilities
Financial organizations are especially exposed due to AI agents processing sensitive customer information and transaction handling. At the same time, healthcare systems leveraging AI for patient engagement and data processing have to deal with possible privacy violations and misinformation spreading by tampered AI output.
Advanced Detection and Mitigation Strategies
Multi-Layered Defense Approaches
Successful protection against prompt injection attacks calls for employing robust, multi-layered security architectures. Input validation and sanitization are the building blocks of defense, utilizing advanced algorithms to identify patterns suggestive of malicious intent.
Yet keyword-based filtering is not enough to counter more advanced obfuscation methods, necessitating more advanced behavior analysis mechanisms.
Adversarial Training and Model Hardening
Adversarial training makes AI models more robust by exposing them to prompt injection attempts while training, enhancing their effectiveness in identifying and fending off manipulation efforts. This method has been seen to hold much promise in recent applications, though no solution offers absolute immunity.
Context-sensitive filtering and behavior surveillance examine not only single prompts but also interaction patterns and contextual relevance. These mechanisms can identify subtle attempts at manipulation that could evade single-input validation controls.
Human-in-the-Loop Security
Incorporating human observation and approval processes for high-risk actions adds another layer of protection. This guarantees that important decisions or delicate operations are subject to human verification even when performed by AI agents, installing an important checkpoint against robotic exploitation.
How OraSec Helps Protect Against AI Security Threats
Organizations seeking to protect their AI systems from prompt injection attacks can benefit from specialized penetration testing services. OraSec provides comprehensive security assessments specifically designed to identify vulnerabilities in AI agent implementations.
Their expert penetration testing team has identified vulnerabilities for over 400 companies worldwide, offering tailored solutions to fortify specific AI-related vulnerabilities. OraSec’s approach includes testing for prompt injection vulnerabilities, assessing AI agent security configurations, and providing actionable recommendations for strengthening defenses against these emerging threats.
Conclusion
Prompt injection attacks evading AI agents are a core security threat that attackers need organizations implementing AI systems to take urgent attention to. The technical intricateness of these attacks, merged with the widening aspect of capabilities within AI agents, poses an advancing threat landscape that existing cybersecurity practices cannot effectively counter.
Organizations need to install extensive security systems, such as multi-tier defenses, routine penetration testing, and ongoing monitoring to safeguard against these new threats. As AI functions become more deeply embedded in core business processes, the need for strong security measures cannot be stressed enough.
Don’t let a security breach reveal your AI vulnerabilities. Consider engaging the services of expert security providers such as OraSec to evaluate and harden your AI agent security posture ahead of the enemy’s hit.